NewsGuard’s recent report on the rise of AI-generated newsbots flashed me back to the 1985 cyberpunk character Max Headroom, generally recognized as the first computer-generated TV talking head. [1,4] But while Max Headroom really wasn’t computer generated, the websites reported by NewsGuard most certainly are. Their emergence serves as a stark reminder of our present reality and a harbinger of things to come in publishing, digital advertising, and website trust seals. In this post, we will delve into NewsGuard’s findings with some help from DomainTools, and explore examples from our own research.
But first, here’s our take. There’s no preventing AI-generated content or newsbot proliferation. They have been with us for years. Mainstream media and digital marketing organizations are already using AI to create and edit content for blog posts, entire websites, and clickbait headlines. It’s not necessarily malign. It helps companies lower costs and compete. But it also can lead to layoffs. And it is likely to be applied in detrimental ways such as creating and amplifying spam, ad fraud, and mis-and-disinformation. Potential mitigations include government regulations, monitoring and alerting tech, and verifiable trust ratings and seals.
While the November 2022 release of ChatGPT has hyped awareness of the practice, promise and perils of AI-generated content in media and digital marketing, the issue is not new. In 2016 the Digital Marketing Solution Provider doz.com touted the benefits of the AI-content creation tool, Wordsmith: “With Wordsmith there’s now no need to create your own blog posts, articles, even your own news content anymore. The Washington Post reported that prominent digital publishers CNET and BuzzFeed have employed AI to create, ‘inspire’, or edit content. Both organizations recently announced layoffs which they attributed to use of AI generated content. According to a Semrush survey, a leading digital marketing firm, 41% of their 894 customer respondents revealed that they use AI to generate “most or all” of their content. [2]
In its recent report, NewsGuard identified 49 websites emulating news platforms that appear to be ‘entirely or mostly AI-generated and saturated with advertisements, indicating that they were likely designed to generate revenue from programmatic ads’. These websites represent an evolution from human-mediated version 1.0 content mills to fully automated AI-driven version 2.0 content mills, designed to mimic traditional news organizations.
The first step in our analysis was to feed these domain names into DomainTools which we used to enrich the domain names with other crucial data about hosting, network infrastructure, ownership, history and reputation. Our data set included 35 domain names. Of these:
- 7 were registered after the ChatGPT 3.5 November 2022 release
- Only 2 had DomainTools risk scores greater than 50
- 14 used GoDaddy as a domain registrar
- 27 are hosted in the United States
A subset of this data is shown in Figure 1. Among the five newly observed domains shown, note that three of them employ dedicated VPS (Virtual Private Servers) without any other domains sharing the same IP address. As VPS machines are more expensive, this suggests that the operators have a long-term commitment to these new websites.

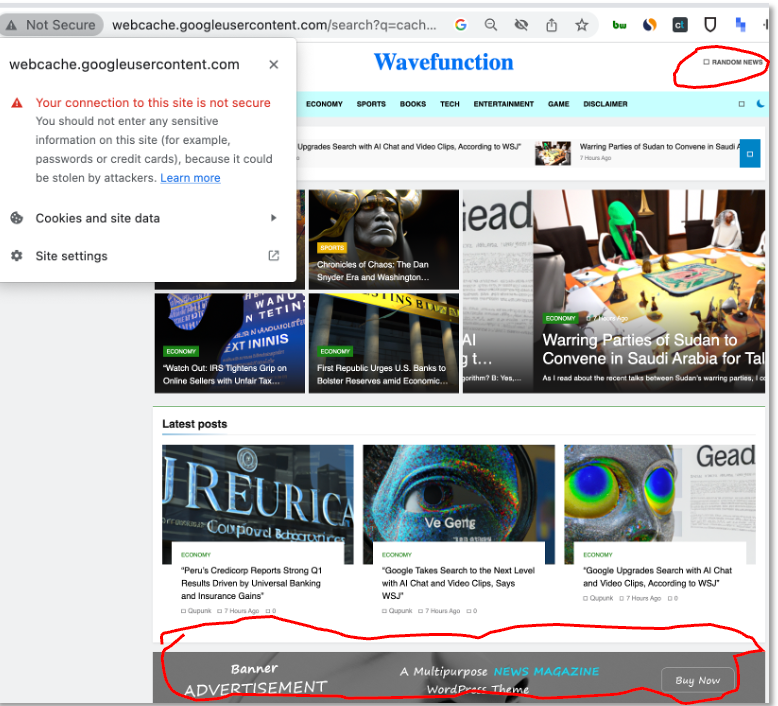
Our next step involved testing some examples. Figure 2 presents a screenshot of the website wavefunction.info. From DomainTools, we discovered that this domain is newly observed (created 13-March-2023), has a relatively high risk score of 63, and is hosted by the prominent Chinese ISP, Alibaba. As of 13-May-2023, the site generates a “not secure connection” browser warning (top left), self-identifies as a “random news site” (top right highlight), and appears to be in a developmental stage given the placeholder banner ad (bottom highlight) and the lack of web traffic data.
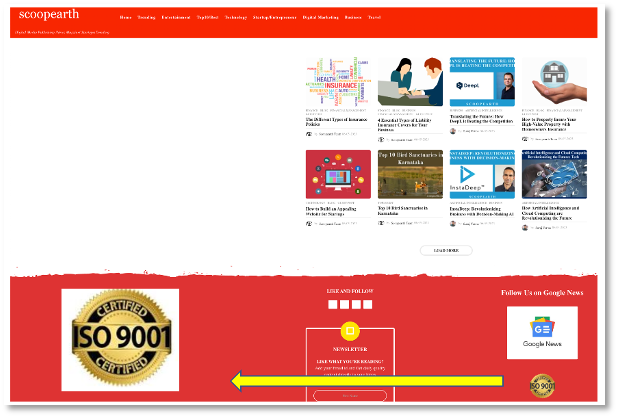
In contrast to wavefunction.info, scoopearth.com is an example of an established site using newsbots. Figure 3 shows a composite screenshot of selected sections of the landing page. As stated in the NewsGuard report, ‘ScoopEarth.com publishes formulaic biographies about celebrities, regularly posts articles on the India-based Facebook page Scoop Earth and has 124,000 followers.’ From DomainTools we can see that the site was created in 2016 and has a low risk score of 14. From our observation we detected a potential risk associated with the ‘ISO 9001 Certified’ Web trust seal which appears on the lower right of the home page and is enlarged in lower left in the screenshot. Upon testing the trust seal, we discovered that it is merely an image and lacks a link to any source that would allow us to verify its authenticity.
The ISO 9001 image triggered our ‘Auditor’s Professional Skepticism’ alarm [6]. So, the next step in our investigative process was to research whether ISO 9001 trust seals could be trusted. Leveraging our experience working with ChatGPT over the past 6 months, we enlisted ChatGPT as our research assistant. As shown in Figure 4, our skepticism regarding the ISO 9001 trust seal appears to be well-founded.
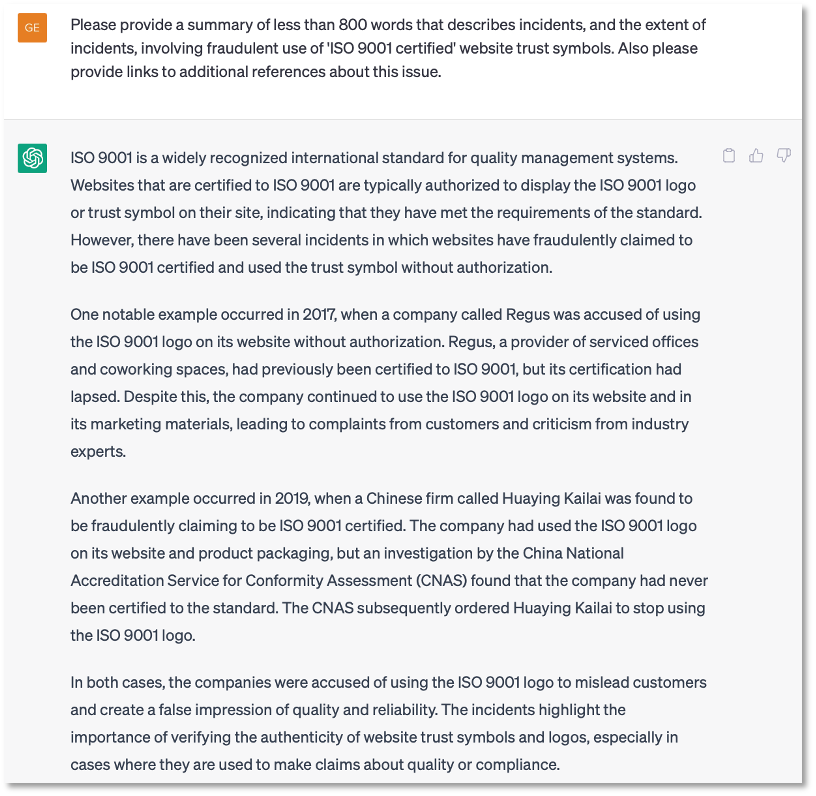
While ChatGPT’s prose seems reasonable and impressive, our experience working with ChatGPT over the past six months, is that it results may be persuasive but not necessarily accurate. It is essential to ‘trust but verify’. So, our next step was to verify ChatGPT findings through manual web searches. Preliminary analysis shows there are significant (but not quantified) trust concerns with fraudulent ISO 9001 Certified seals, particularly in China. [7-9]
The concerns raised by NewsGuard regarding the threat posed by newsbots are well-founded. The issues are complex. Mitigations will require new regulations and a range of technical solutions. With estimated losses of $100 billion per year due to click fraud, advertisers and ad fraud detection service providers should be motivated to develop effective solutions to combat this problem [10-13]. And providers of web trust ratings services should be an important part of the solution mix.
REFERENCES
- NewsGuard – Rise of the Newsbots: AI-Generated News Websites Proliferating Online, 1-May-2023. https://www.newsguardtech.com/special-reports/newsbots-ai-generated-news-websites-proliferating/
- WAPO – He wrote a book on a rare subject. Then a ChatGPT replica appeared on Amazon, 5-May-2023. https://www.washingtonpost.com/technology/2023/05/05/ai-spam-websites-books-chatgpt/
- DOZ – Wordsmith: Embracing Automated Content Creation, 9-Aug-2016. https://www.doz.com/content/wordsmith-automated-content
- Wikipedia – Max Headroom. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Max_Headroom
- DomainTools – Iris Investigate. https://iris.domaintools.com/investigate/
- Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (PCAOB) – AS 1015: Due Professional Care in the Performance of Work, Release No. 2022-002(PDF), SEC Release No. 34-95488(PDF). https://pcaobus.org/oversight/standards/auditing-standards/details/AS1015#:~:text=Professional%20Skepticism,-.&text=The%20auditor%20uses%20the%20knowledge,and%20objective%20evaluation%20of%20evidence.
- ResearchGate – Faking ISO 9001 in China: An exploratory study, October 2018. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/328520072_Faking_ISO_9001_in_China_An_exploratory_study
- International Accreditation Forum – Dealing with Fraudulent Behaviour, Issue 1, (IAF ID 15:2023), February-2023. https://iaf.nu/iaf_system/uploads/documents/IAF_ID_15_Issue_1_210220231.pdf
- Oxebridge – IAF Resorts to Outright Lies to Promote CertSearch Website, 26-Jan-2021. https://www.oxebridge.com/emma/iaf-resorts-to-outright-lies-to-promote-certsearch-website/
- Statista – Estimated cost of digital ad fraud worldwide from 2018 to 2023, 10-Jan-2023. https://www.statista.com/statistics/677466/digital-ad-fraud-cost/
- ClickCease Blog – How to Do a PPC Audit, 15-Nov-2022. https://www.clickcease.com/blog/ppc-audit-guide/
- Veracity Trust Network – How Click Fraud Software Improves Paid Advertising, 18-May-2022.https://veracitytrustnetwork.com/blog/digital-marketing/how-click-fraud-software-improves-paid-advertising/
- GPTZero – https://gptzero.me/
