In our previous post we reviewed the findings of NewsGuard’s report on the use of AI-generated content by news and information websites. In this post we’ll analyze, with help from DomainTools and ChatGPT: new reporting from NewsGuard, AI-generated content detection tools and methods, and implications for ad fraud solution providers. Here are the key insights:
- an increase in AI-generated content in both traditional media and content farms is inevitable but not necessarily a cybersecurity threat
- ad fraud is a cybersecurity threat that will be exacerbated by AI-generated content
- cyber threat intelligence providers could leverage methods and data from content detection, SEO (Search Engine Optimization), and click fraud solution providers.
In the May 19 follow-up report NewsGuard found 125 more ‘unreliable AI-generated Sites (UAINs)’, an increase of 155% over the previous two weeks. These UAIN sites are ‘entirely or mostly generated by AI tools’. The intent is to generate clickbait articles to attract programmatic ads. Effectively, these sites serve inauthentic content to facilitate ad fraud. [1]
While NewsGuard did not provide domain indicators of compromise (IOCs) in its public report, we were able to identify UAIN domain names using human inference, ChatGPT, and some of the google dork methods described by ShadowDragon and DorkSearch as described in the following scenario. [2-4]
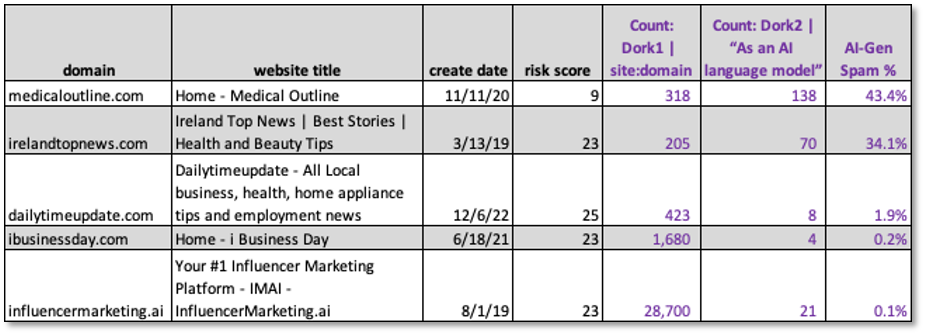
The table in Figure 1 provides a summary of our analysis. The five domain names in column 1 were easily inferred by human analysis of the NewsGuard report. The next step was to feed the domain names into the DomainTools Iris tool for enrichment. While DomainTools provides data on hundreds of network, registration, and reputation attributes, for our simple scenario we selected the attributes shown in fields 1-4 of the table. Two surprising observations of note:
- From column 3 (create date): Of the 5 domains shown, only 1 was created after the November 2022 release of ChatGPT. This suggests that the sites had an established history and do not appear to have been created as unsupervised content farms
- From column 4 (risk score): These sites all have relatively low risk scores (< 70). DomainTools risk scores measure malware, spam, phishing and proximity. They are not designed to rate for inauthentic content.
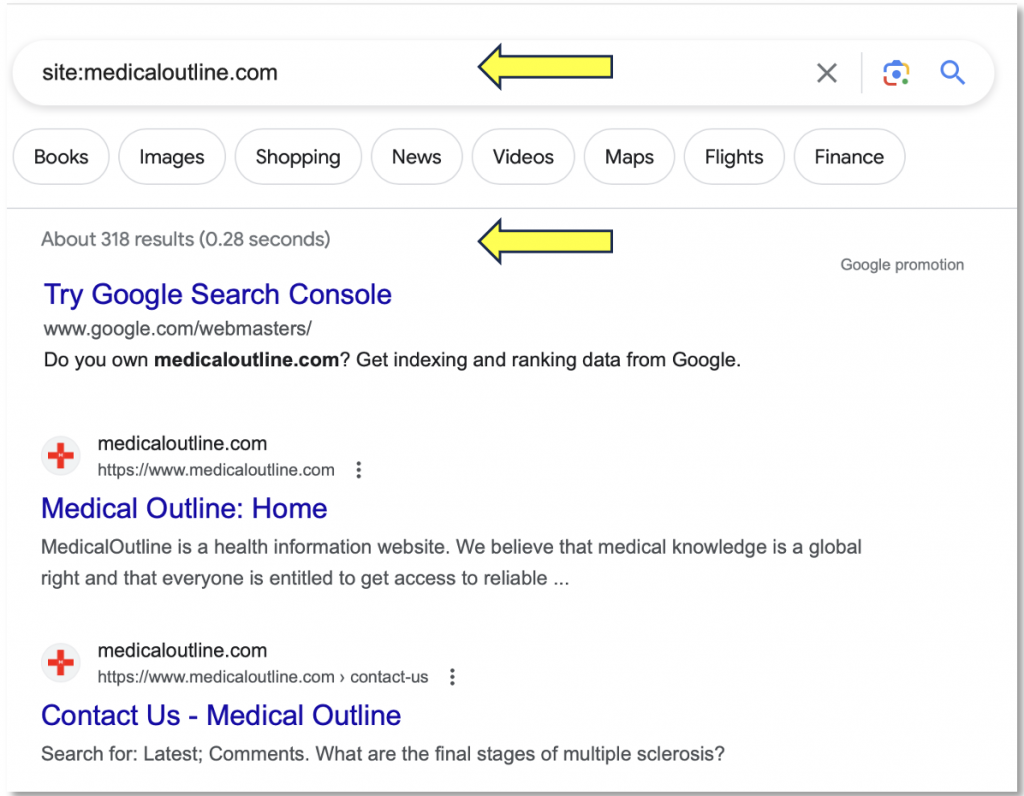
The next step in our scenario is to test some of the Google ‘search operators’ (AKA Dorks) that could be used to identify UAIN sites as described in references 2-4. The site:domain operator returns all “search results from the particular domain, URL, or URL prefix specified in the operator.” In Figure we see all results for the domain ‘medicaloutline.com’. As shown in Figure 1, column 5, the total is 318.
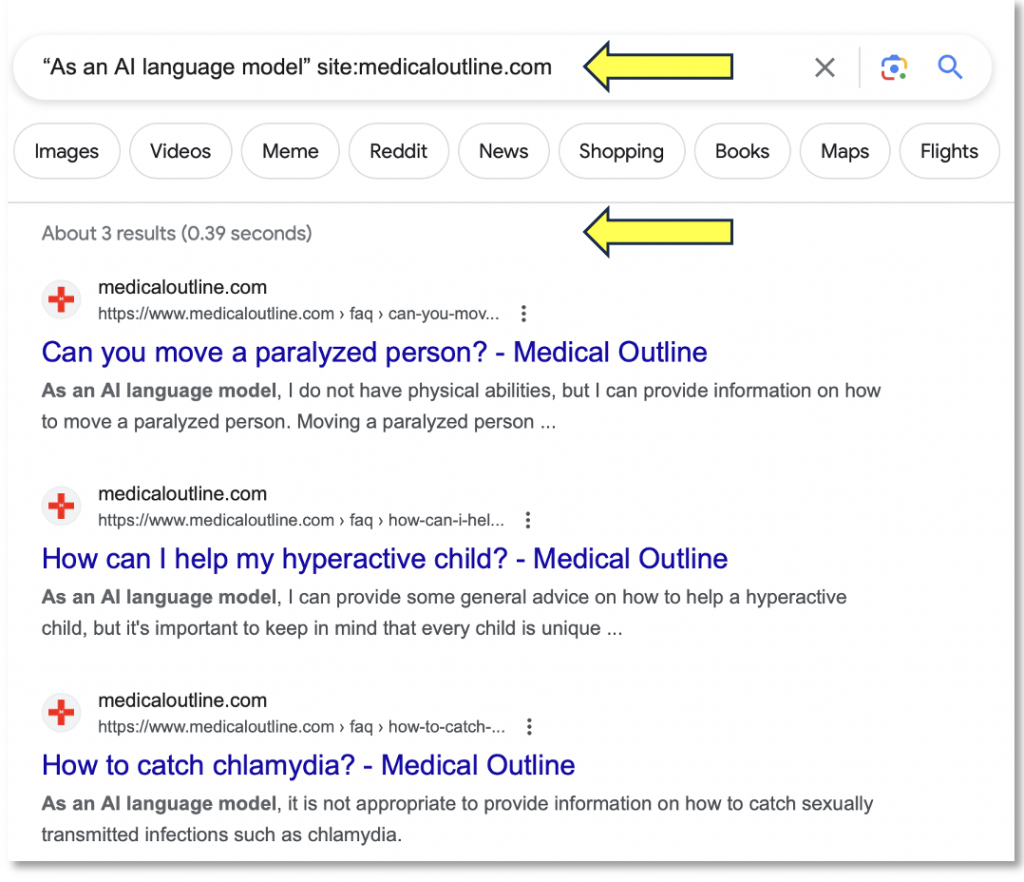
The previous dork will generate all results. To narrow our search for posts that may have been generated by AI, we can add the phrase “As an AI language model”. Note that this query generated only three results.
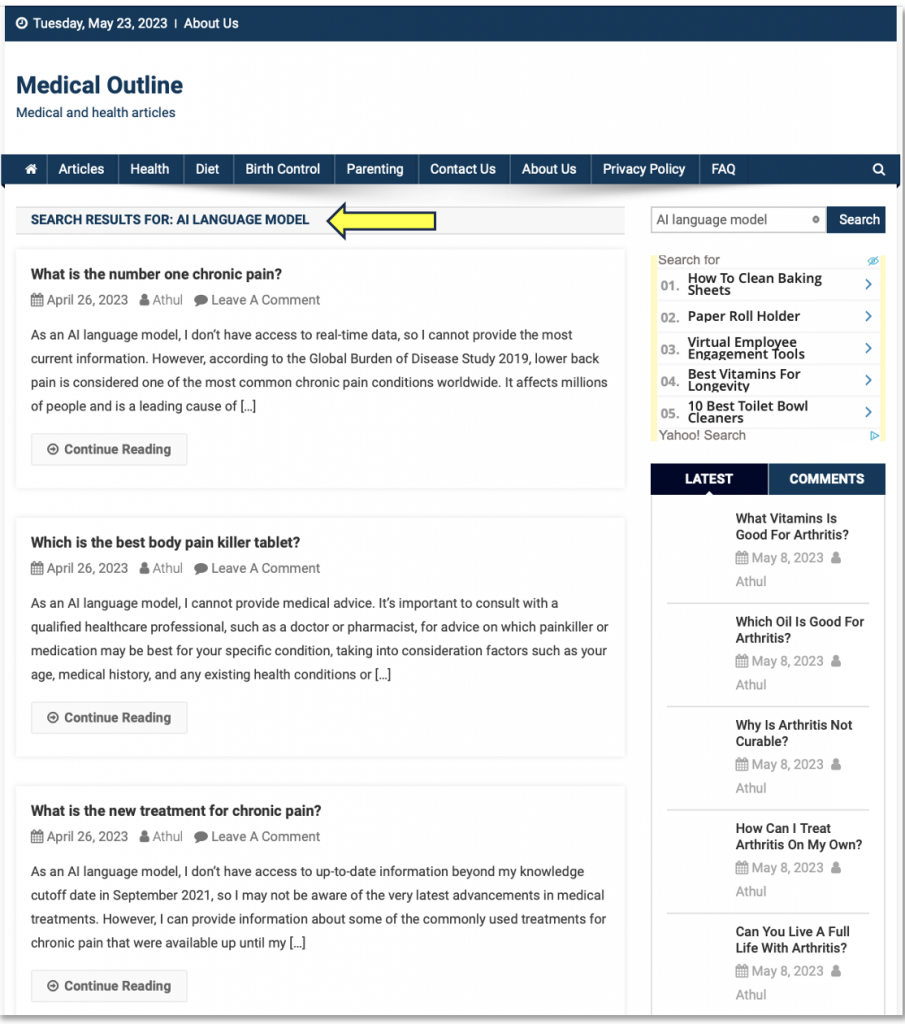
When we verified the results by searching the site directly for the phrase ‘As an AI language model’, we actually found 138 posts by the same author (Athul) between April 4 and May 8 (Figure 4). This suggests that this dork generated a high number of false negatives resulting in poor search coverage.
To complete Table 1, we manually plugged these queries as Dork 1 and Dork 2 into Columns 5 and 6. Finally, we computed an ‘AI-Gen Spam’ ratio and plugged into column 7. While this non-random sample of 5 sites is too small to make reliable conclusions, our findings suggest that none of these websites are fully AI automated content farms.
The examples above were intended to test the feasibility of using Dorks to identify inauthentic content on websites and social media sites. Our preliminary assessment is that more work is needed to determine the efficacy and efficiency of these methods.
As noted in our previous post, AI-content generators are not new and are used by some prominent media and publishing sites like BuzzFeed and CNET. Automated tools for detecting AI-generated content and ad fraud are well established in the SEO and Digital Ad Tech markets. [7-12] The application of SEO and Ad Tech to cyber threat intelligence is a topic we may consider in future posts.
We’ll conclude with an acknowledgement of the patient and valuable market research, tutoring, and editing assistance we received from ChatGPT as shown in Figures 5 and 6.

REFERENCES
- NewsGuard – NewsGuard Now Identifies 125 News and Information Websites Generated by AI, Develops Framework for Defining ‘Unreliable AI-Generated News’ and Information Sources, 19-May-2023. https://www.newsguardtech.com/press/newsguard-now-identifies-125-news-and-information-websites-generated-by-ai-develops-framework-for-defining-unreliable-ai-generated-news-and-information-sources/
- ShadowDragon.io: A Practical Guide for OSINT Investigators to Combat Disinformation and Fake Reviews Driven by AI (ChatGPT) , May 2023. https://info.shadowdragon.io/hubfs/SD_APracticalGuide_WhitePaper-1.pdf
- DorkSearch.com – Unlocking ChatGPT: Advanced AI for Google Dorking & OSINT, 17-Jan-2023. https://dorksearch.com/blog/chatgpt-advanced-ai-google-dorking/
- NYTimes – A.I.-Generated Content Discovered on News Sites, Content Farms and Product Reviews, 19-May-2023. https://www.nytimes.com/2023/05/19/technology/ai-generated-content-discovered-on-news-sites-content-farms-and-product-reviews.html
- Demandsage.com – 11 Best AI Content Detectors 2023 (Editors Choice), 21-April-2023. https://www.demandsage.com/ai-content-detectors/
- Wired.com – How to Detect AI-Generated Text, According to Researchers, 8-Feb-2023. https://www.wired.com/story/how-to-spot-generative-ai-text-chatgpt/
- Youtube.com – Lori Ballen: Google Can Detect AI Generated Content – Here’s Why It’s Dangerous, 10-Dec-2022. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=194AMlfMkMo
- theTradeDesk – https://www.thetradedesk.com/us/about-us/industry-initiatives/marketplace-quality
- DoubleVerify – https://doubleverify.com/innovations/
- Malwarebytes Labs – AI-powered content farms start clogging search results with ad-stuffed spam, 4-May-2023. https://www.malwarebytes.com/blog/news/2023/05/ai-generated-content-farms-fill-search-results-with-advert-stuffed-spam
- Cloudflare – What is click fraud? | How click bots work. https://www.cloudflare.com/learning/bots/what-is-click-fraud/#:~:text=One%20example%20of%20click%20fraud,%22click%22%20on%20those%20ads.
- Cloudflare – What is Ad fraud? https://www.cloudflare.com/learning/bots/what-is-ad-fraud/
- DomainTools – Iris Investigate. https://iris.domaintools.com/investigate/
