Do you want to know how to crack down on oligarchs who evade sanctions? Recent research suggests that targeting their secret networks of offshore financial intermediaries could be the key. In this post, we’ll explore the findings and show you how ChatGPT and DomainTools can help.
According to a recent study by researchers at USC and Dartmouth [1,2], sanctions programs aimed at Russian oligarchs have been largely ineffective due to the opaqueness of their offshore networks. This is backed up by reports from organizations like the Council on Foreign Relations [3] and Thomson Reuters [4]. To uncover these networks, the USC-Dartmouth team used qualitative and quantitative social network analysis on a big data collection sourced from the Offshore Leaks Database provided by the International Consortium of Investigative Journalists (ICIJ). This collection includes details on 810,000 offshore companies, foundations, and trusts. The researchers identified 6,300 relationships connecting oligarchs to 510 intermediaries.
For Russian oligarchs’ offshore networks, the high-connectivity nodes consisting of a small group of wealth managers, represent a serious vulnerability which should be targeted by investigators. A summary of the mostly highly connected Intermediary organizations used by Russian oligarchs is shown in the table below (table 2 in the USC-Dartmouth research).
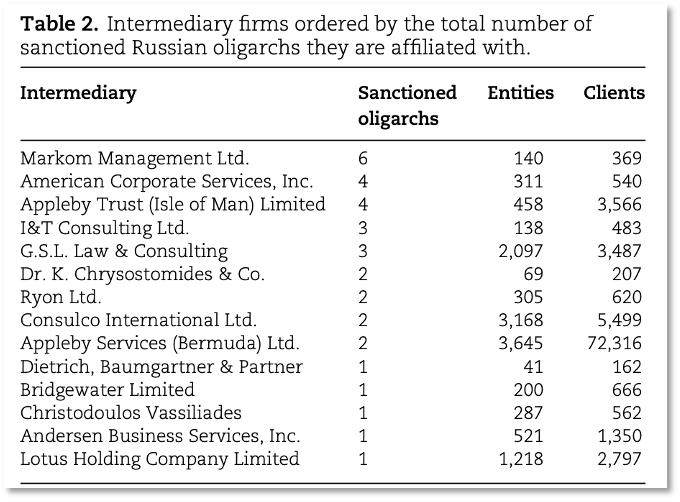
This may be a nice list for researchers and policy purposes, but cybercrime investigations also need the domain names and IP addresses for evidence. Once investigators have this basic evidence, they can get warrants so they can proceed with other investigative steps, like shutting down websites or seizing computers, software and data. Collecting the essential network infrastructure needed for cyber investigations is a simple task with ChatGPT and DomainTools, as shown in the following examples.
The Table below was generated by ChatGPT. I asked it to “give me a 3-column list for the following entities, where column 1 is ‘entity name’, column 2 is ‘entity website’ and column 3 is ‘entity country’. Then I gave it the intermediaries I wanted it to look up. The query results are shown below.
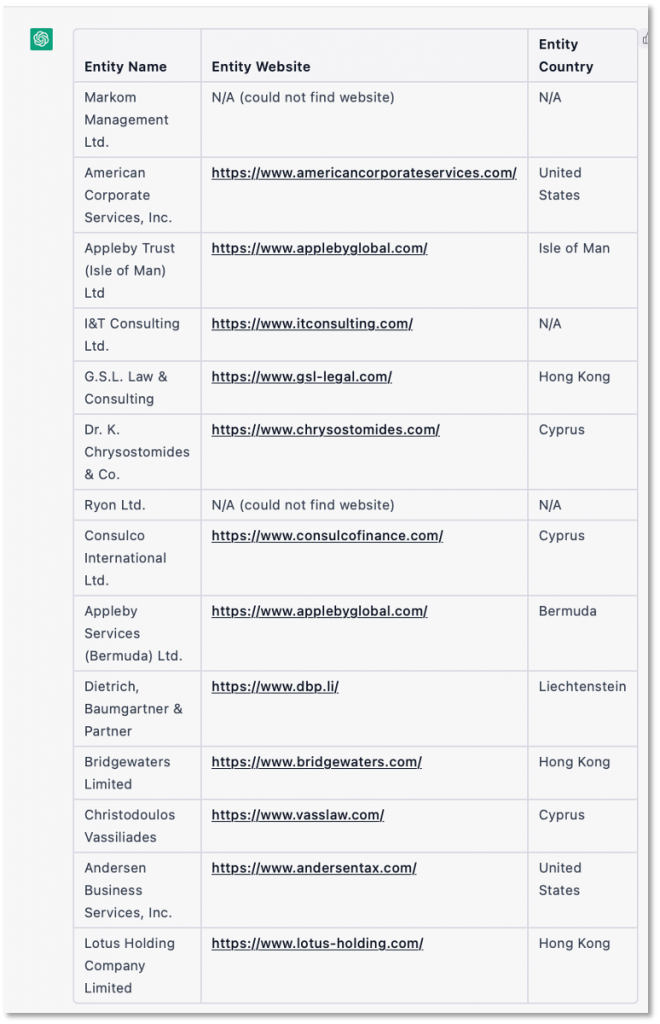
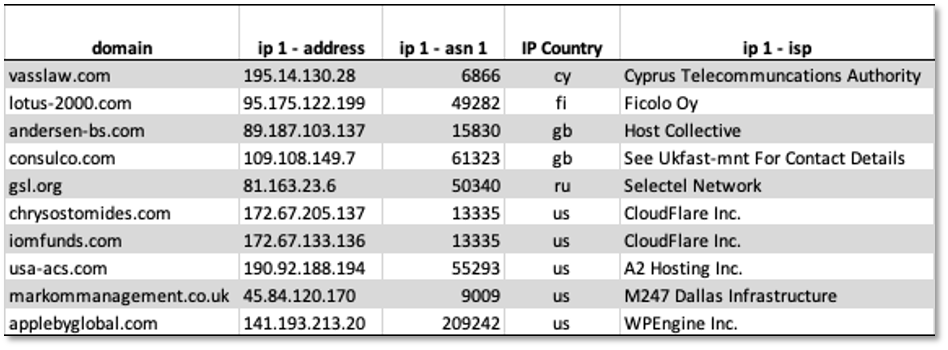
Getting the website domain names is a good start, investigators need more information about the intermediary network infrastructure, such as the IP address, hosting provider or ISP, country where the host is registered, domain name registrar, domain name registrant and more. For this information, the investigator can feed the domain names to DomainTools to pull an expanded set of network indicators. The table below is a small subset of information generated by DomainTools for these intermediaries. Even from this subset, we can see how US investigators could prioritize the intermediary infrastructure located in the US and share the non-US intermediaries with partners in cooperative countries.
Conclusion: This research is highly relevant to cyber investigators and groups responsible for sanctions policy and enforcement. The use of tools like ChatGPT and DomainTools is just the beginning. As we continue to uncover the secrets of oligarch offshore networks, how can we use technology to create a more transparent and just global financial system? Stay tuned for more examples in future posts.
PS: In addition to using ChatGPT as an assistant to do simple lookups, I also used it as a copy-editor. It did a good job. It did not make any substantive changes, introduce new facts, or hallucinate. Most of the changes were style tweaks. Some of the recommendations improved readability. So, credit to ChatGPT for rewriting: the Title and paragraphs 1 and 2 (though I found a word-confusion error in #2). It also found that the “conclusion is good, but it could be more compelling. Consider ending with a call to action or a thought-provoking question.” I followed some of its suggestions.
REFERENCES:
- Ho-Chun Herbert Chang, Brooke Harrington, Feng Fu, Daniel N Rockmore. Complex systems of secrecy: the offshore networks of oligarchs. ‘PNAS Nexus, Volume 2, Issue 3, March 2023. https://academic.oup.com/pnasnexus/article/2/3/pgad051/7059318
- Supplementary Information for Complex Systems of Secrecy: The Offshore Networks of Oligarchs. https://academic.oup.com/pnasnexus/article/2/3/pgad051/7059318#supplementary-data
- Council on Foreign Relations – One Year of War in Ukraine: Are Sanctions Against Russia Making a Difference? 21-Feb-2023. https://www.cfr.org/in-brief/one-year-war-ukraine-are-sanctions-against-russia-making-difference
- Thomson Reuters – The fog of sanctions: Global banks and businesses face unprecedented challenges in applying measures against Russia, 20-July-2022. https://www.thomsonreuters.com/en-us/posts/wp-content/uploads/sites/20/2022/07/Russia-Sanctions-White-Paper-2022.pdf
- Forbes Magazine – The Forbes ultimate guide to Russian oligarchs, 7-April-2022. https://www.forbes.com/sites/giacomotognini/2022/04/07/the-forbes-ultimate-guide-to-russian-oligarchs/?sh=9255a1e276d9
- Amato N. 2022. US sanctions ban provision of accounting, consulting services to Russia. J Account Res. https://www.journalofaccountancy.com/news/2022/may/us-sanctions-ban-provision-accounting-consulting-services-russia.html
- Dominguez D, et al. 2020. Panama papers’ offshoring network behavior. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2405844020311373
- Wikipedia – Bahamas Leaks. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bahamas_Leaks
- OFAC (Office of Foreign Assets Control) – Sanctions List, search. https://sanctionssearch.ofac.treas.gov/Default.aspx
- International Consortium of Investigative Journalists. 2022 Apr. List of oligarchs and Russian elites featured in ICIJ investigations. 42 Tognini G, Hyatt J. 2022 Feb. https://www.icij.org/investigations/russia-archive/list-of-oligarchs-and-russian-elites-featured-in-icij-investigations/
- International Consortium of Investigative Journalists – How a network of enablers have helped Russia’s oligarchs hide their wealth abroad, 2-March. https://www.icij.org/investigations/russia-archive/how-a-network-of-enablers-have-helped-russias-oligarchs-hide-their-wealth-abroad/
- GitHub – ICIJ/offshoreleaks-data-packages. https://github.com/ICIJ/offshoreleaks-data-packages/find/0cc45b5c14c6dacf518f199a3d15ef1c2d5f2fb9
- McKinsey & Company – The fight against money laundering: Machine learning is a game changer, 7-Oct-2022. https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/risk-and-resilience/our-insights/the-fight-against-money-laundering-machine-learning-is-a-game-changer
