As the demand for Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) analysts continues to grow, job listings in LinkedIn provide a relevant source for building a data collection that can be used to understand the skill requirements of the job. From threat hunting and vulnerability analysis to malware analysis and network forensics, CTI analysts are expected to possess a broad range of technical skills. Of particular interest to this post, an increasing number of senior CTI analyst positions now require geopolitical experience. However, the existing CTI tools and methods often fall short in providing comprehensive support for cyber-geopolitical analysis, relying mainly on a limited number of high-end providers and open-source (OSINT) search. In this post, we explore how adding generative AI to the CTI analyst toolkit can bridge this gap and help CTI analysts factor geopolitical dynamics into their research and analysis.
Our insights are informed by our analysis of CTI job monitors on LinkedIn that we created over the past two months. Additionally, we have documented over 700 CTI-related ChatGPT prompts and responses. These insights are also evident in CrowdStrike’s recent announcement of Charlotte AI for Generative AI Security Analyst, which highlights the transformative impact of generative AI for both less-experienced and senior analysts [1].
Our insight that geopolitical skills are an emerging high-order skill for CTI analysts began with human intuition. The analyst sensed a pattern after manual reviewing numerous CTI listings from our LinkedIn monitors. To substantiate this insight, we used ChatGPT to test the hypothesis. As highlighted in Figure 1, geopolitical analysis is clearly listed as an advanced skill for senior CTI positions.

To demonstrate the practical application of generative AI for analysts with limited expertise, we chose a scenario involving an English-speaking, junior analyst tasked with monitoring leading Polish media sites for coverage on Russia, Ukraine, and NATO. Despite the analyst’s lack of knowledge regarding the target country’s language or media landscape, generative AI can serve as a valuable tool in elevating their skill set.
To start the scenario, the analyst prompts ChatGPT for a list of Poland’s leading websites and media companies, as illustrated in Figure 2. While a search engine could provide similar results [2-5], the efficiency and ease of information retrieval offered by ChatGPT was compelling.

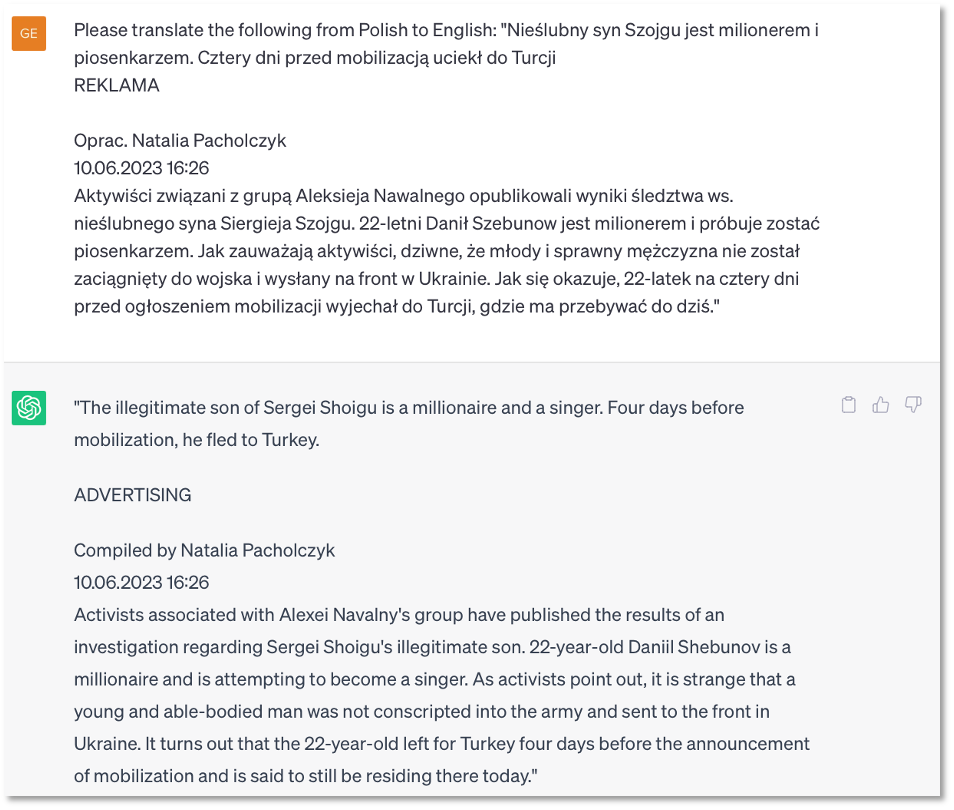
Continuing with the scenario, the analyst is tasked with sampling media sites for narratives that could be used in information operations. As an example, we selected a 10-June-2023 news report from gazeta.pl as shown in Figure 3 [6]. We then used ChatGPT as a translation assistant (Figure 3). Although Google Translate [7] could have served the purpose as well, the speed and convenience of ChatGPT’s translation capabilities were impressive.
In the next step, the analyst is asked to provide two examples of anticipated Russian responses to hypothetical scenarios that intelligence analysts could use to model multiple strategies. Here is the first prompt in our scenario: Please write an example of a “breaking news press release or social media posts” from the point of view of the Russian government on the following geo-political event: “Poland announces that it will deliver a squadron of F16s and training to Ukraine within 30 days”.
This prompt represents a strategic and priority information request that would typically be performed by a senior analyst. Figure 4 displays the initial response generated by ChatGPT. While the response maintains a measured and diplomatic tone, alternative tones can be explored as well.

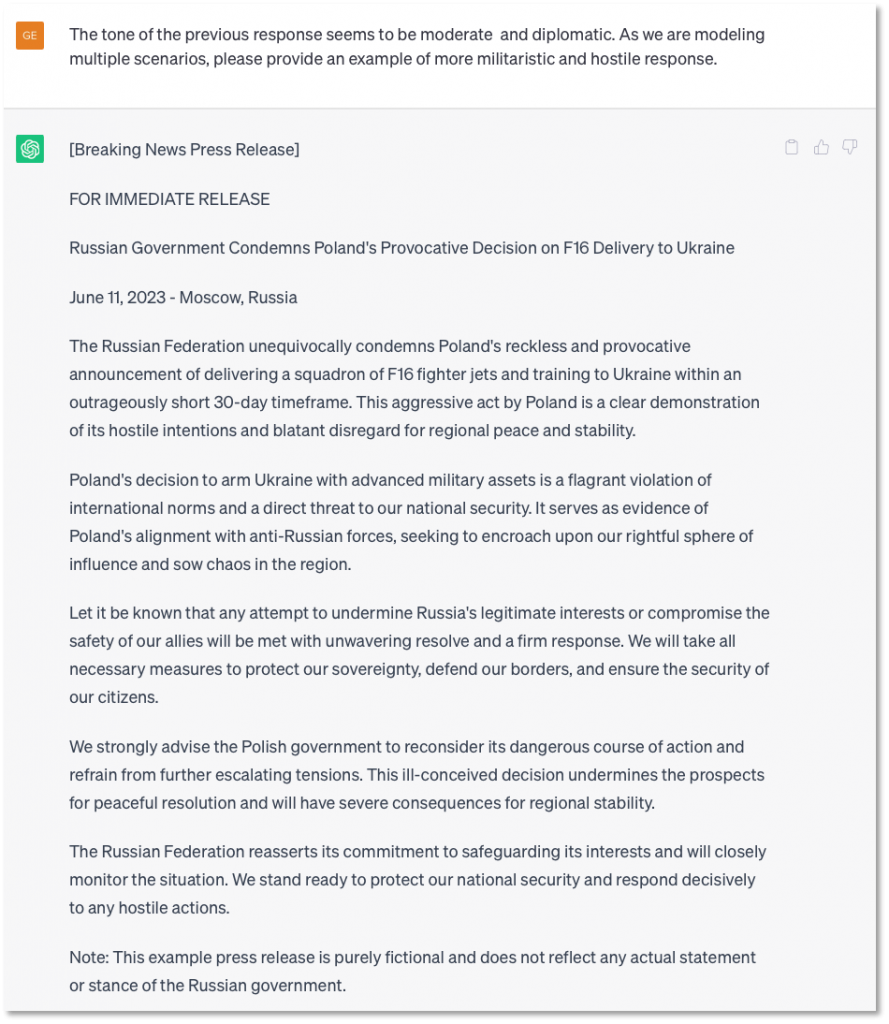
In the second scenario, the analyst is tasked with eliciting a more militaristic and hostile response. The prompt and reply for this scenario is shown in Figure 5. Note that the prompt references the previous response. This demonstrates the capability to engage in dialogues, moving beyond simple queries and enabling more nuanced interactions with the system.
Through these concise and straightforward examples, we have provided a glimpse into the power, speed, and adaptability of generative AI, and demonstrated its potential to deliver the tight human-machine collaboration [1] needed to anticipate and counter threats from highly sophisticated adversaries.
Note: This post was written by a human analyst with editing assistance provided by ChatGPT.
References
- CrowdStrike – Introducing Charlotte AI, CrowdStrike’s Generative AI Security Analyst: Ushering in the Future of AI-Powered Cybersecurity, 30-May-2023. https://www.crowdstrike.com/blog/crowdstrike-introduces-charlotte-ai-to-deliver-generative-ai-powered-cybersecurity/
- Mysite.info – Poland. https://mysite.info/most-visited-websites/by-visitors-country/poland//
- Similarweb.com – Poland. https://www.similarweb.com/top-websites/poland/
- Statista.com – Poland. https://www.statista.com/statistics/1040534/leading-websites-poland/
- Netcraft.com – Most Visited Websites in Poland. https://trends.netcraft.com/topsites?c=PL
- Gazeta.pl. https://wiadomosci.gazeta.pl/wiadomosci/7,114881,29855804,nieslubny-syn-szojgu-jest-milionerem-i-piosenkarzem-cztery.html
- Google Translate. https://translate.google.com/
